VARGA 1. THE BIRTH.
(There was) a descendant of the Ikshvâku 1 (family), an invincible 2 Sâkya monarch, pure in mind (mental gifts) and of unspotted virtue, called therefore 'Pure-rice' (Suddhodana). . 1
Joyously reverenced by all men (or, 'beings'), as the new moon (is welcomed by the world), the king indeed (was) like the heaven-ruler Sakra 3, his queen like (the divine) Sakî. . 2
Strong and calm of purpose as the earth, pure in mind as the water-lily, her name, figuratively assumed, Mâyâ, she was in truth incapable of class-comparison. . 3
p. 2
On her in likeness as the heavenly queen descended the spirit and entered her womb. A mother, but free from grief or pain, (she was) without any false or illusory 1 mind. . 4
Disliking the clamorous ways of the world, (she remembered) the excellent garden of Lumbinî, a pleasant spot, a quiet forest retreat, (with its) trickling fountains, and blooming flowers and fruits. . 5
Quiet and peaceful, delighting in meditation, respectfully she asked the king for liberty to roam therein; the king, understanding her earnest desire, was seized with a seldom-felt anxiety (to grant her request). . 6
He commanded his kinsfolk, within and without (the palace), to repair with her to that garden shade; and now the queen Mâyâ knew that her time for child-bearing was come. . 7
She rested calmly on a beautiful couch, (surrounded by) a hundred thousand female attendants; (it was) the eighth day of the fourth moon, a season of serene and agreeable character. . 8
Whilst she (thus) religiously observed 2 the rules of a pure discipline, Bodhisattva was born from her right side, (come) to deliver the world, constrained by great pity, without causing his mother pain or anguish. . 9
As king Yu-liu 3 was born from the thigh, as king Pi-t’au 4 was born from the hand, as king Man-to 5
p. 3
was born from the top of the head, as king Kia-k’ha 1 was born from the arm-pit, . 10
So also was Bodhisattva on the day of his birth produced from the right side; gradually emerging from the womb, he shed in every direction the rays of his glory. . 11
As one (born) from recumbent space 2, and not through the gates of life, through countless kalpas, practising virtue, self-conscious he came forth to life, without confusion. . 12
Calm and collected, not falling headlong (was he born), gloriously manifested, perfectly adorned, sparkling with light he came from the womb 3, as when the sun first rises (from the East). . 13
(Men) indeed regarded 4 his exceeding great glory, yet their sight remained uninjured: he allowed them to gaze, the brightness of his person concealed for the time, as when we look upon the moon in the heavens. . 14
His body, nevertheless, was effulgent with light, and like the sun which eclipses the shining of the lamp, so the true gold-like beauty of Bodhisattva shone forth and was diffused everywhere. . 15
Upright and firm and unconfused in mind, he deliberately took seven steps 5, the soles of his feet
p. 4
resting evenly upon the ground as he went, his footmarks remained bright as seven stars. . 16
Moving like the lion, king of beasts, and looking earnestly towards; the four quarters, penetrating to the centre the principles of truth, he spake thus with the fullest assurance: . 17
'This birth is in the condition of a Buddha 1; after this I have done with renewed birth; now only am I born this once, for the purpose of saving all the world.' . 18
And now from the midst of heaven there descended two streams of pure water, one warm, the other cold, and baptized his head 2, causing refreshment to his body. . 19
And now he is placed in the precious palace hall, a jewelled couch for him to sleep upon, and the heavenly kings with their golden flowery hands hold fast the four feet of the bed. . 20
Meanwhile the Devas in space, seizing their jewelled canopies, attending, raise in responsive harmony their heavenly songs, to encourage him to accomplish his perfect purpose 3. . 21
Then the Nâga-râgas filled with joy, earnestly desiring to show their reverence for the most excellent law 4, as they had paid honour to the former Buddhas, now went to meet Bodhisattva; . 22
p. 5
They scattered before him Mandâra flowers, rejoicing with heartfelt joy to pay such religious homage; (and so, again,) Tathâgata having appeared in the world, the Suddha 1 angels rejoiced with gladness; . 23
With no selfish or partial joy, but for the sake of religion they rejoiced, because creation 2, engulfed in the ocean of pain, was now to obtain perfect release. . 24
Then the precious Mountain-râga, Sume(ru) 3, firmly holding this great earth 4 when Bodhisattva appeared in the world, was swayed by the wind of his perfected merit. . 25
On every hand the world was greatly shaken, as the wind drives the tossing boat; so also the minutest atoms of sandal perfume, and the hidden sweetness of precious lilies, . 26
Floated on the air and rose through space and then commingling came back to earth; so again the garments of Devas descending from heaven touching the body, caused delightful thrills of joy; . 27
The sun and moon with constant course redoubled the brilliancy of their light, whilst in the world the
p. 6
fire's gleam of itself prevailed without the use of fuel. . 28
Pure water, cool and refreshing from the springs, flowed here-and there, self-caused; in the palace all the waiting women were filled with joy at such an unprecedented event. . 29
Proceeding all in company, they drink and bathe themselves; in all arose calm and delightful thoughts; countless inferior Devas (bhûtas), delighting in religion, like clouds assembled. . 30
In the garden of Lumbinî, filling the spaces between the trees, rare and special flowers, in great abundance, bloomed out of season. . 31
All cruel and malevolent kinds of beings, together conceived a loving heart; all diseases and afflictions among men without a cure applied, of themselves were healed. . 32
The various cries and confused sounds of beasts were hushed and silence reigned; the stagnant water of the river-courses flowed apace, whilst the polluted streams became clear and pure. . 33
No clouds gathered throughout the heavens, whilst angelic music, self-caused, was heard around; the whole world of sentient creatures enjoyed peace and universal tranquillity. . 34
Just as when a country visited by desolation, suddenly obtains .an enlightened ruler, so when Bodhisattva was born, he came to remove the sorrows of all living things. . 35
Mâra 1, the heavenly monarch, alone was grieved and rejoiced not. The Royal Father (Suddhodana)
p. 7
beholding his son 1, strange and miraculous 2, as to his birth, . 36
Though self-possessed and assured in his soul, was yet moved with astonishment and his countenance changed, whilst he alternately weighed with himself the meaning (of such an event), now rejoiced and now distressed. . 37
The queen-mother beholding her child, born thus contrary to laws of nature, her timorous woman's heart was doubtful; her mind through fear, swayed between extremes: . 38
Not distinguishing the happy from the sad portents, again and again she gave way to grief 3; and now the aged women of the world, (of the 'long night 4') in a confused way supplicating heavenly guidance, . 39
Implored the gods to whom their rites were paid, to bless the child; (cause peace to rest upon the royal child.) Now there was at this time in the grove, a certain soothsayer 5, a Brahman, . 40
Of dignified mien and wide-spread renown, famed for his skill and scholarship: beholding the signs 6, his
p. 8
heart rejoiced, and he exulted at the miraculous event. . 41
Knowing the king's mind to be somewhat perplexed, he addressed him (thus) with truth and earnestness, 'Men born in the world, chiefly desire to have a son the most renowned 1; . 42
'But now the king, like the moon when full, should feel in himself a perfect joy, having begotten an unequalled 2 son, (for by this the king) will become illustrious among his race; . 43
'Let then his heart be joyful and glad, banish all anxiety and doubt, the spiritual omens that are everywhere, manifested indicate for your house and dominion a course of continued prosperity 3. . 44
'The most excellently endowed child now born will bring deliverance to the entire world 4, none but a heavenly teacher has a body such as this 5, golden colour’d, gloriously resplendent. . 45
'One endowed with such transcendent marks, must reach the state of "Samyak 6-Sambodhi," or if he be induced to engage in worldly delights, then he must become a universal monarch 7; . 46
p. 9
'Everywhere recognised as the ruler of the great earth, mighty in his righteous government, as a monarch ruling the four empires 1, uniting under his sway all other rulers; . 47
'As among all lesser lights, the sun's brightness is by far the most excellent. But if he seek a dwelling among the mountain forests, with single heart searching for deliverance 2, . 48
'Having arrived at the perfection of true wisdom, he will become illustrious 3 throughout the world; for as mount Sumeru is monarch among all mountains, . 49
'Or, as gold is chief among all precious things, or, as the ocean is supreme among all streams 4, or, as the moon is first among the stars, or, as the sun is brightest of all luminaries, . 50
'So Tathâgata, born in the world, is the most eminent 5 of men; his eyes clear and expanding 6, the lashes both above and below moving with the lid, . 51
'The iris of the eye of a clear blue colour 7, in shape like the moon when half full, such characteristics as these, without contradiction, foreshadow the most excellent condition of perfect (wisdom).' 52.
p. 10
At this time the king addressed the twice-born 1, 'If it be as you say, with respect to these miraculous signs, that they indicate such consequences, . 53
'Then no such case has happened with former kings, nor down to our time has such a thing occurred.' The Brahman addressed the king thus, 'Say not so; for it is not right; . 54
'For with regard to renown and wisdom, personal celebrity, and worldly substance, these four things indeed are not to be considered according to precedent or subsequence; . 55
'But whatever is produced according to nature 2, such things are liable to the law of cause and effect: but now whilst I recount some parallels let the king attentively listen; . 56
'Bhrigu, Aṅgira 3 (Aṅgiras?), these two of Rishi family 4, having passed many years apart from men, each begat an excellently-endowed son, . 57
'Brihaspati with Sukra, skilful in making royal treatises, not derived from former families (or, tribes); . 58
'Sârasvata, the Rishi, whose works 5 have long disappeared, begat a son, Po-lo-sa 6, who compiled illustrious Sutras 7 and Shâstras; . 59
p. 11
'That which now we know and see, is not therefore dependent on previous connection; Vyâsa, the Rishi, the author of numerous treatises, . 60
'After his death had among his descendants, Poh-mi (Vâlmîki), who extensively collected Gâthâ sections; Atri, the Rishi, not understanding the sectional treatise on medicine, . 61
'Afterwards begat Âtreya, who was able to control diseases; the twice-born Rishi Kusi (Kusika), not occupied with heretical treatises, . 62
'Afterwards (begat) Kia-ti-na râga, who thoroughly understood heretical systems; the sugar-cane monarch 1, who began his line, could not restrain the tide of the sea, . 63
'But Sagara-râga, his descendant, who begat a thousand royal sons, he could control the tide of the great sea so that it should come no further. . 64
'Ganaka, the Rishi, without a teacher acquired power of abstraction. All these, who obtained such renown, acquired powers of themselves 2; . 65
'Those distinguished before, were afterwards forgotten; those before forgotten, became afterwards distinguished 3; kings like these and godlike Rishis have no need of family inheritance, . 66
'And therefore the world need not regard those going before or following. So, mighty king! is it with you, you should experience true joy of heart, . 67
'And because of this joy should banish for ever doubt or anxiety.' The king hearing the words
p. 12
of the seer was glad, and offered him increased gifts 1. . 68
'Now have I begotten a valiant (excellent) son (he said), who will establish a wheel authority, whilst I, when old and grey-headed, will go forth to lead a hermit's life 2, . 69
'So that my holy king-like son may not give up the world and wander through mountain forests.' And now near the spot within the garden, there was a Rishi, leading the life of an ascetic 3; . 70
His name was Asita, wonderfully skilful in the interpretation of signs; he approached the gate of the palace; the king (beholding him) exclaimed, 'This is none other but Brahmadeva, . 71
'Himself enduring penance from love of true religion, these two characteristics 4 so plainly visible as marks of his austerities.' Then the king was much rejoiced; . 72
And forthwith he invited him within the palace, and with reverence set before him entertainment, whilst he, entering the inner palace, rejoiced only (in prospect of) seeing the royal child. . 73
Although surrounded by the crowd of court-ladies, yet still he was as if in desert solitude; and now they place a preaching throne and pay him increased honour and religious reverence, . 74
As Antideva râga reverenced the priest Vasishtha. Then the king addressing the Rishi, said, 'Most fortunate am I, . 75
'Great Rishi! that you have condescended to
p. 13
come here to receive from me becoming gifts and reverence; I pray you therefore enter on your exhortation.' . 76
Thus requested and invited the Rishi felt unutterable joy, and said, 'All hail, ever victorious monarch! possessed of all noble (virtuous) qualities 1, . 77
'Loving to meet the desires of those who seek, nobly generous in honouring the true law, conspicuous as a race for wisdom and humanity, with humble mind you pay me homage, as you are bound. . 78
'Because of your righteous deeds in former lives 2, now are manifested these excellent fruits; listen to me, then, whilst I declare the reason of the present meeting. . 79
'As I was coming on the sun's way 3, I heard the Devas in space declare that the king had born to him (begotten) a royal son, who would arrive at perfect intelligence 4; . 80
'Moreover I beheld such other portents 5, as have
p. 14
constrained me now to seek your presence; desiring to see the Sâkya monarch who will erect the standard of the true law.' . 81
The king hearing the Rishi's. words was fully assured; escaping from the net of doubt, he ordered an attendant to bring the prince, to exhibit him to the Rishi. . 82
The Rishi, beholding the prince, the thousand-rayed wheel on the soles of his feet, the web-like filament between his fingers 1, between his eyebrows the white 2 wool-like prominence, . 83
His privy parts hidden as those of the horse, his complexion bright and lustrous; seeing these wonderful birth-portents, the seer wept and sighed deeply. . 84
The king beholding the tears of the Rishi, thinking of his son, his soul was overcome, and his breath fast held his swelling heart. Thus alarmed and ill at ease, . 85
Unconsciously he arose from his seat, and, bowing his head at the Rishi's feet he addressed him in these words, 'This son of mine, born thus wonderfully, . 86
'Beautiful in face, and surpassingly graceful, little different from the gods in form, giving promise of superiority in the world, ah! why has he caused thee grief and pain? . 87
'Forbid it, that my son should die! (should be short-lived!)--(the thought) creates in me grief and
p. 15
anxiety; that one athirst, within reach of the eternal draught 1, should after all reject and lose it! sad indeed! . 88
'Forbid it, he should lose his wealth and treasure! dead to his house! lost to his country! for he who has 2 a prosperous son in life, gives pledge that his country's weal is well secured; . 89
'And then, coming to die, my heart will rest content, rejoicing in the thought. of offspring surviving me; even as a man possessed of two eyes, one of which keeps watch, while the other sleeps; . 90
'Not like the frost-flower of autumn, which though it seems to bloom, is not a reality. A man who, midst his tribe and kindred, deeply loves a spotless son, . 91
'At every proper time in recollection of it has joy; O! that you would cause me to revive 3!' The Rishi, knowing the king-sire to be thus greatly afflicted at heart, . 92
Immediately addressed the Maharâga: 'Let not the king be for a moment anxious! the words I have spoken to the king, let him ponder these, and not permit himself to doubt; . 93
'The portents now are as they were before, cherish
p. 16
then no other thoughts! But recollecting I myself am old, on that account I could not hold my tears; . 94
'For now my end is coming on. But this son of thine will rule the world, born for the sake of all that lives 1! this is indeed one difficult to meet with; . 95
'He shall give up his royal estate, escape from the domain of the five desires 2, with resolution and with diligence practise austerities, and then awakening, grasp the truth. . 96
'Then constantly, for the world's sake (all living things), destroying the impediments of ignorance and darkness, he shall give to all enduring light, the brightness of the sun of perfect wisdom. . 97
'All flesh submerged in the sea of sorrow; all diseases collected as the bubbling froth; decay and age like the wild billows; death like the engulfing ocean; . 98
'Embarking lightly in the boat of wisdom he will save the world from all these perils, by wisdom stemming back the flood. His, pure teaching like to the neighbouring shore, . 99
'The power of meditation, like a cool lake, will be enough for all the unexpected birds; thus deep and full and wide is the great river of the true law; . 100
'All creatures parched by the drought of lust may freely drink thereof, without stint; those
p. 17
enchained in the domain of the five desires, those driven along by many sorrows, . 101
'And deceived amid the wilderness of birth and death, in ignorance of the way of escape, for these Bodhisattva has been born in the world, to open out a way of salvation 1. . 102
'The fire of lust and covetousness, burning with the fuel of the objects of sense, (on the flames) he has caused the cloud of his mercy to rise, so that the rain of the law may extinguish them. . 103
'The heavy gates of gloomy unbelief, fast kept by covetousness and lust, within which are confined all living things, he opens and gives free deliverance. . 104
'With the tweezers of his diamond wisdom he plucks out the opposing principles of lustful desire. In the self-twined meshes of folly and ignorance all flesh poor and in misery, helplessly (lying), . 105
'The king of the law has come forth, to rescue these from bondage. Let not the king in respect of this his son encourage in himself one thought of doubt or pain; . 106
'But rather let him grieve on account of the world, led captive by desire, opposed to truth; but I, indeed, amid the ruins of old age and death, am far removed from the meritorious condition of the holy one 2, . 107
'Possessed indeed of powers of abstraction, yet
p. 18
not within reach of the gain he will give, to be derived from his teaching as the Bodhisattva; not permitted to hear his righteous law, . 108
'My body worn out, after death, alas! (destined) to be born as a Deva 1 still liable to the three calamities (old age, decay, and death), (therefore I weep).' The king and all his household attendants, hearing the words of the Rishi, . 109
Knowing the cause of his regretful sorrow, banished from their minds all further anxiety: 'And now (the king. said) to have begotten this excellent son, gives me rest at heart; . 110
'But that he should leave his kingdom and home, and practise the life of an ascetic, not anxious to ensure the stability of the kingdom, the thought of this still brings with it pain.' . 111
At this time the Rishi, turning to the king with true words, said, 'It must be even as the king anticipates, he will surely arrive at perfect enlightenment.' . 112
Thus having appeased every anxious heart among the king's household, (the Rishi) by his own inherent spiritual power ascended into space and disappeared. . 113
At this time Suddhodana râga, seeing the excellent marks (predictive signs) of his son, and, moreover, hearing the words of Asita, certifying that which would surely happen, . 114
Was greatly affected with reverence to the child, he redoubled measures for its protection, and (was
p. 19
filled) with constant thought; (moreover) he issued decrees through the empire, to liberate all captives in prison, 115.
According to the custom when a (royal) son was born, giving the usual largess, in agreement with the directions of the Sacred Books, and extending his gifts to all; (or, all these things he did completely). . 116
The child 1 when ten days old, (his father's) mind being now quite tranquil, he announced a sacrifice to all the gods, and prepared to give liberal offerings to all the religious bodies; . 117
Srâmanas and Brâhmanas invoked by their prayers a blessing from the gods, whilst he bestowed gifts on the royal kinspeople and the ministers and the poor within the country; . 118
The women who dwelt in the city or the villages, (all those who needed) cattle or horses or elephants or money, each, according to his necessities, was liberally supplied; . 119
Then selecting by divination a lucky time, they took the child back to his own palace; with a double-feeding white-pure-tooth 2, carried in a richly-adorned chariot (cradle), . 120
With ornaments of every kind and colour round his neck; shining with beauty, exceedingly resplendent with unguents. The queen embracing
p. 20
him in her arms, going around, worshipped the heavenly spirits. . 121
Afterwards she remounted her precious chariot, surrounded by her waiting women; the king, with his ministers and people, and all the crowd of attendants, leading the way and following, . 122
Even as the ruler of heaven, Sakra, is surrounded by crowds of Devas; as Mahesvara, when suddenly his six-faced child was born, . 123
Arranging every kind of present, gave gifts, and asked for blessings; so now the king, when his royal son was born, made all his arrangements in like manner; . 124
So Vaisravana, the heavenly king, when Nalakûvara 1 was born, surrounded by a concourse of Devas, was filled with joy and much gladness; . 125
So the king, now the royal prince was born, in the kingdom of Kapila, his people and all his subjects were likewise filled with joy. . 126
VARGA 2. LIVING IN THE PALACE.
And now in the household of Suddhodana râga, because of the birth of the royal prince, his clansmen and younger brethren (namesakes), with his ministers, were all generously disposed, . 127
Whilst elephants, horses and chariots and the wealth of the country and precious 2 vessels, daily increased and abounded, being produced wherever requisite 3; . 128
p. 21
So too countless hidden treasures came of themselves from the earth. From the midst of the pure snowy mountains, a wild herd of white elephants, . 129
Without noise, of themselves, came; not curbed by any, self-subdued, every kind of colour’d 1 horse, in shape and quality surpassingly excellent, . 130
With sparkling jewelled manes and flowing tails, came prancing round, as if with wings; these too, born in the desert, came at the right time, of themselves. . 131
A (herd of) pure-colour’d, well-proportioned cows, fat and fleshy, and remarkable for beauty, giving fragrant and pure milk with equal flow, came together in great number 2 at this propitious time: . 132
Enmity and envy gave way to peace; content and rest prevailed on every side, whilst there was closer union amongst the true of heart, discord and variance were entirely appeased; . 133
The gentle air distilled a seasonable rain, no crash of storm or tempest was heard, the springing seeds, not waiting for their time, grew up apace and yielded abundant increase; . 134
The five cereals grew ripe with scented grain, soft and glutinous, easy of digestion; all creatures big with young, possessed their bodies in ease and their frames well-gathered; . 135
All men, even those who had not received the seeds of instruction derived from the four holy
p. 22
ones 1; all these, throughout the world, born under the control of selfish appetite, without any thought for others' goods, . 136
Had no proud, envious longings; no angry, hateful thoughts. All men and women 2 were grave (profound) as the first man of the age (kalpa). . 137
All the temples of the gods and sacred shrines, the gardens, wells, and fountains, all these like things in heaven, produced of themselves, at the proper time, (their several adornments). . 138
There was no famishing hunger, the soldiers' weapons were at rest, all diseases disappeared; throughout the kingdom all the people were bound close in family love and friendship; . 139
Piously affectioned they indulged in mutual pleasures, there were no impure or polluting desires, they sought their daily gain righteously, no covetous money-loving spirit prevailed, . 140
But with religious purpose they gave liberally; there was no thought of any reward (return), but all practised the four rules of purity; and every hateful thought was suppressed and destroyed. . 141
Even as in days gone by, Manu râga begat a child (called) 'Brilliancy of the Sun,' on which there prevailed through the country great prosperity, and all Wickedness came to an end; . 142
p. 23
So now the king having begotten a royal prince, these marks of prosperity were seen; and because of such a concourse of propitious signs, the child was named Siddhârtha 1. . 143
And now his royal mother, the queen Mâyâ, beholding her son born under such circumstances, beautiful as a child of heaven, adorned with every excellent distinction, . 144
From excessive joy which could not be controlled died, and was born in heaven 2. Then Pragâpatî Gautamî, beholding the prince, like an angel, . 145
With beauty seldom seen on earth, seeing him thus born and now his mother dead, loved and nourished him as her own child; and the child regarded her as his mother. . 146
So as the light of the sun or the moon, little by little increases, the royal child also increased each day in every mental excellency and beauty of person; . 147
(His body exhaled) the perfume of priceless sandal wood, (decorated with) the famed Gambunada gold (gems); divine medicines (there were) to preserve him in health, glittering necklaces upon his person; . 148
The members of tributary states, hearing that
p. 24
the king had an heir born to him, sent their presents and gifts of various kinds, oxen, sheep, deer, horses, and chariots, . 149
Precious vessels and elegant ornaments, fit to delight the heart of the prince; but though presented with such pleasing trifles, the necklaces and other pretty ornaments, . 150
The mind (nature) of the prince was unmoved, his bodily frame small indeed, but his heart established; his mind at rest within its own high purposes 1, was not to be disturbed by glittering baubles. . 151
And now he was brought to learn the useful arts, when lo! once instructed (at one hearing) he surpassed his teachers. His father, the king, seeing his exceeding talent, and his deep purpose to have done with the world and its allurements, . 152
Began to enquire as to the names of those in his tribe who were renowned for elegance and refinement. Elegant and graceful, and a lovely maiden, was she whom they called Yasodharâ; . 153
In every way fitting to become a consort for the prince; and to allure by pleasant wiles his heart. The prince with a mind so far removed (from the world), with qualities so distinguished, and with so charming an appearance, . 154
Like the elder son of Brahmadeva, Sanatkumâra (She-na Kiu-ma-lo); the virtuous damsel, lovely and refined, gentle and subdued in manner; . 155
Majestic like the queen of heaven, constant ever,
p. 25
cheerful night and day, establishing the palace in purity and quiet, full of dignity and exceeding grace, . 156
Like a lofty hill rising up in space 1; or as a white autumn cloud; warm or cool according to the season; choosing a proper dwelling according to the year, . 157
Surrounded by a return of singing women, who join (their voices) in harmonious heavenly concord, without any jarring or unpleasant sound, exciting (in the hearers) forgetfulness of worldly cares. . 158
As the heavenly Gandharvas 2 of themselves in their beauteous palaces (cause) the singing women to raise heavenly strains, the sounds of which and their beauty ravish both eyes and heart; . 159
(So) Bodhisattva dwelt in his lofty palace, with music such as this. The king his father, for the prince's sake, dwelt purely in his palace, practising every virtue; . 160
Delighting 3 in the teaching of the true law, he 4 put away from him every evil companion, (that) his heart might not be polluted by lust; regarding inordinate desire as poison, . 161
Keeping his passion and his body in due control, destroying and repressing all trivial thoughts, desiring to enjoy virtuous conversation, loving 5 instruction (fit) to subdue the hearts of men, . 162
p. 26
Aiming to accomplish the conversion of unbelievers; removing all schemes of opposition 1 (from whatever source they came), by the enlightening power of his doctrine, aiming to save the entire world; (thus he desired) that the body of people should obtain rest; . 163
Even as we desire to give peace to our children, so did he long to give rest to the world 2. He also attended to his religious duties (sacrificing by fire to all the spirits), with clasped hands adoring the moon (drinking the moon's brightness); . 164
Bathing his body in the waters of the Ganges; cleansing his heart in the waters of religion, performing his duties with no private aim, but regarding his child and the people at large, . 165
Loving righteous conversation 3, righteous words with loving (aim), loving words with no mixture of falsehood, true words imbued by love, . 166
And yet withal so modest and self-distrustful, unable on that account to speak as confident of truth; loving to all, and yet not loving the world, with no thought of selfishness or covetous desire, . 167
Aiming to restrain the tongue and in quietness to find rest from wordy contentions, not seeking in the
p. 27
multitude of religious duties to condone for a worldly principle in action 1; . 168
But aiming to benefit the world, by a liberal and unostentatious charity; the heart without any contentious thought, but resolved by goodness to subdue the contentious, . 169
Composing the one 2, whilst protecting the seven, removing the seven, guarding and adjusting the five, reaching to the three, by having learned the three, knowing the two, and removing the two; . 170
Desiring to mortify the passions, and to destroy every enemy of virtue, not multiplying coarse or unseemly words, but exhorting to virtue in the use of courteous language, . 171
Full of sympathy and ready charity, pointing out and practising the way of mutual dependence, receiving and understanding the wisdom of spirits and Rishis, crushing and destroying every cruel and hateful thought; . 172
Thus his fame and virtue were widely renowned, (and yet himself) finally (or, for ever) separate from the ties of the world, showing the ability of a master builder, laying a good foundation of virtue, an example for all the earth; . 173
So a man's heart composed and at rest, his limbs and all his members will also be at ease. And now
p. 28
the son of Suddhodana, and his virtuous wife Yasodharâ, . 174
As time went on, growing to full estate, their child Râhula was born; and then Suddhodana râga considered thus, 'My son, the prince, having a son born to him, . 175
'The affairs of the empire will be handed down in succession, and there will be no end to its righteous government; the prince having begotten a son, will love his son as I love him 1, . 176
'And no longer think about leaving his home as an ascetic, but devote himself to the practice of virtue; I now have found complete rest of heart, like one just born to heavenly joys.' . 177
Like as in the first days of the kalpa, Rishi-kings by the way in which (they walked), practising pure and spotless deeds, offered up religious offerings, without harm to living thing, . 178
And illustriously prepared an excellent karma, so the king excelling in the excellence of purity 2, in family and excellency of wealth, excelling in strength and every exhibition of prowess, . 179
Reflected the glory of his name through the world, as the sun sheds abroad his thousand rays. But now, being the king of men (or, a king among men), he deemed it right to exhibit his son's (prowess), . 180
For the sake of his family and kin, to exhibit him; to increase his family's renown, his glory spread so high as even to obtain the name of 'God begotten;' and having partaken of these heavenly joys, . 181
p. 29
Enjoying the happiness of increased wisdom; understanding the truth, by his own righteousness derived from previous hearing of the truth; the reward of previous acts, widely known 1. . 182
Would that this might lead my son (he prayed) to love his child and not forsake his home; the kings of all countries, whose sons have not yet grown up, . 183
Have prevented them exercising authority in the empire, in order to give their minds relaxation, and for this purpose have provided them with worldly indulgences, so that they may perpetuate the royal seed; . 184
So now the king, having begotten a royal son, indulged him in every sort of pleasure; desiring that he might enjoy these worldly delights, and not wish to wander from his home in search of wisdom; . 185
In former times the Bodhisattva kings, although their way (life) has been restrained (severe), have yet enjoyed the pleasures of the world, and when they have begotten a son, then separating themselves from family ties, . 186
Have afterwards entered the solitude of the mountains, to prepare themselves in the way of a silent recluse. . 187
VARGA 3. DISGUST AT SORROW 2.
Without are pleasant garden glades, flowing fountains, pure refreshing lakes, with every kind of
p. 30
flower, and trees with fruit, arranged in rows, deep shade beneath. . 188
There, too, are various kinds of wondrous birds, flying and sporting in the midst, and on the surface of the water the four kinds of flowers, bright colour’d, giving out their floating scent; . 189
Minstrel maidens 1 cause their songs, and chorded music, to invite the prince. He, hearing the sounds of singing, sighs for the pleasures of the garden shades, . 190
And cherishing within these happy thoughts 2, he dwelt upon the joys of an outside excursion; even as the chained elephant ever longs for the free desert wilds. . 191
The royal father, hearing that the prince would enjoy to wander through the gardens, first ordered all his attendant officers to adorn and arrange them, after their several offices: . 192
To make level and smooth the king's highway, to remove from the path all offensive matter, all old persons, diseased or deformed, all those suffering through poverty or great grief, . 193
So that his son in his present humour might see nothing likely to afflict his heart. The adornments being duly made, the prince was invited to an audience; . 194
The king seeing his son approach, patted his head and looking at the colour of his face, feelings of sorrow and joy intermingled, bound him. His mouth willing to speak, his heart restrained. . 195
(Now see) the jewel-fronted gaudy chariot; the four equally-pacing, stately horses; good-tempered
p. 31
and well-trained; young and of graceful appearance; . 196
Perfectly pure and white, and draped with flowery coverings. In the same chariot stands the (stately) driver; the streets were scattered over with flowers; precious drapery fixed on either side of the way, . 197
With dwarfed trees lining the road, costly vessels employed for decoration, hanging canopies and variegated banners, silken curtains, moved by the rustling breeze, . 198
Spectators arranged on either side of the path. With bodies bent and glistening eyes, eagerly gazing, but not rudely staring, as the blue lotus flower (they bent) drooping in the air, . 199
Ministers and attendants flocking round him, as stars following the chief of the constellation 1; all uttering the same suppressed whisper of admiration, at a sight so seldom seen in the world; . 200
Rich and poor, humble and exalted, old and young and middle-aged, all paid the greatest respect, and invoked blessings on the occasion: . 201
So the country-folk and the town-folk, hearing that the prince was coming forth, the well-to-do not waiting for their servants, those asleep and awake not mutually calling to one another, . 202
The six kinds of creatures not gathered together and penned, the money not collected and locked up, the doors and gates not fastened, all went pouring along the way on foot; . 203
The towers were filled and the mounds by the trees, the windows and the terraces along the streets; with bent body fearing to lift their eyes, carefully
p. 32
seeing that there was nothing about them to offend, . 204
Those seated on high addressing those seated on the ground, those going on the road addressing those passing on high, the mind intent on one object alone; so that if a heavenly form had flown past, . 205
Or a form entitled to highest respect, there would have been no distraction visible, so intent was the body and so immovable the limbs. And now beautiful as the opening lily, . 206
He advances towards the garden glades, wishing to accomplish the words of the holy prophet (Rishi). The prince seeing the ways prepared and watered, and the joyous holiday appearance of the people, . 207
(Seeing too) the drapery and the chariot pure, bright, shining, his heart exulted greatly and rejoiced. The people (on their part) gazed at the prince, so beautifully adorned, with all his retinue, . 208
Like an assembled company of kings (gathered) to see a heaven-born prince. And now a Deva-râga of the Pure abode, suddenly appears by the side of the road; . 209
His form changed into that of an old man, struggling for life, his heart weak and oppressed. The prince seeing the old man, filled with apprehension, asked his charioteer, . 210
'What kind of man is this? his head white and his shoulders bent, his eyes bleared and his body withered, holding a stick to support him along the way. . 211
'Is his body suddenly dried up by the heat, or has he been born in this way?' The charioteer, his heart much embarrassed, scarcely dared to answer truly, . 212
p. 33
Till the pure-born (Deva) added his spiritual power, and caused him to frame a reply in true words: 'His appearance changed, his vital powers decayed, filled with sorrow, with little pleasure, . 213
'His spirits gone, his members nerveless, these are the indications of what is called "old age." This man was once a sucking child, brought up and nourished at his mother's breast, . 214
'And as a youth full of sportive life, handsome, and in enjoyment of the five pleasures; as years passed on, his frame decaying, he is brought now to the waste of age.' . 215
The prince greatly agitated and moved, asked his charioteer another question and said, 'Is yonder man the only one afflicted with age, or shall I, and others also, be such as he?' . 216
The charioteer again replied and said, 'Your highness also inherits this lot, as time goes on, the form itself is changed, and this must doubtless come, beyond all hindrance: . 217
'The youthful form must wear the garb of age, throughout the world, this is the common lot.' Bodhisattva, who had long prepared the foundation of pure and spotless wisdom, . 218
Broadly setting the root of every high quality, with a view to gather large fruit in his present life, hearing these words respecting the sorrow of age, was afflicted in mind, and his hair stood up-right. . 219
Just as the roll of the thunder and the storm alarm and put to flight the cattle; so was Bodhisattva affected by the words; shaking with apprehension, he deeply sighed; . 220
Constrained at heart because of the pain of 'age;'
p. 34
with shaking head and constant gaze, he thought upon this misery of decay; what joy or pleasure can men take (he thought), . 221
In that which soon must wither, stricken by the marks of age; affecting all without exception; though gifted now with youth and strength, yet not one but soon must change and pine away. . 222
The eye beholding such signs as these before it, how can it not be oppressed by a desire to escape 1? Bodhisattva then addressed his charioteer, `Quickly turn your chariot and go back, . 223
'Ever thinking on this subject of old age approaching, what pleasures now can these gardens afford, the years of my life like the fast-flying wind; turn your chariot, and with speedy wheels take me to my palace.' . 224
And so his heart keeping in the same sad tone, (he was) as one who returns to a place of entombment; unaffected by any engagement or employment, so he found no rest in anything within his home. . 225
The king hearing of his son's sadness urged (his companions) to induce him again to go abroad, and forthwith incited his ministers and attendants to decorate the gardens even more than before. . 226
The Deva then caused himself to appear as a sick man; struggling for life, he stood by the wayside, his body swollen and disfigured, sighing with deep-drawn groans, . 227
His hands and knees contracted and sore with disease, his tears flowing as he piteously muttered (his petition). The prince asked his charioteer, 'What sort of man, again, is this?' . 228
p. 35
Replying he said, 'This is a sick man. The four elements all confused and disordered, worn and feeble, with no remaining strength, bent down with weakness, looking to his fellow-men for help.' . 229
The prince hearing the words thus spoken, immediately became sad and depressed in heart, and asked, 'Is this the only man afflicted thus, or are others liable to the same (calamity)?' . 230
In reply he said, 'Through all the world, men are subject to the same condition; those who have bodies must endure affliction, the poor and ignorant, as well as the rich and great.' . 231
The prince, when these words met his ears, was oppressed with anxious thought and grief; his body and his mind were moved throughout, just as the moon upon the ruffled tide. . 232
'Placed thus in the great furnace of affliction, say! what rest or quiet can there be! Alas! that worldly men, (blinded by) ignorance and oppressed with dark delusion, . 233
'Though the robber sickness may appear at any time, yet live with blithe and joyous hearts!' On this, turning his chariot back again, he grieved to think upon the pain of sickness. . 234
As a man beaten and wounded sore, with body weakened, leans upon his staff, so dwelt he in the seclusion of his palace, lone-seeking, hating worldly pleasures. . 235
The king hearing once more of his son's return, asked anxiously the reason why, and in reply was told--'he saw the pain of sickness.' The king in fear like one beside himself, . 236
Roundly blamed the keepers of the way; his heart constrained, his lips spoke not; again he
p. 36
increased the crowd of music women, the sounds of merriment twice louder than aforetime, . 237
If by these sounds and sights (the prince) might be gratified; and indulging worldly feelings, might not hate his home. Night and day the charm of melody increased, but his heart was still unmoved by it. . 238
The king himself then went forth to observe everything successively, and to make the gardens even yet more attractive, selecting with care the attendant women, that they might excel in every point of personal beauty; . 239
Quick in wit and able to arrange matters well, fit to ensnare men by their winning looks; he placed additional keepers along the king's way, he strictly ordered every offensive sight to be removed, . 240
And earnestly exhorted the illustrious coachman, to look well and pick out the road as he went. And now that Deva of the pure abode, again caused the appearance of a dead man; . 241
Four persons carrying the corpse lifted it on high, and appeared (to be going on) in front of Bodhisattva; the surrounding people saw it not, but only Bodhisattva and the charioteer; . 242
(Once more) he asked, 'What is this they carry? with streamers and flowers of every choice description, whilst the followers are overwhelmed with grief, tearing their hair and wailing piteously.' . 243
And now the gods instructing the coachman, he replied and said, 'This is a "dead man," all his powers of body destroyed, life departed; his heart without thought, his intellect dispersed; . 244
'His spirit gone, his form withered and decayed; stretched out as a dead log; family ties broken
p. 37
[paragraph continues] --all his friends who once loved him, clad in white cerements, . 245
'Now no longer delighting to behold him, remove him to lie in some hollow ditch (tomb).' The prince hearing the name of DEATH, his heart constrained by painful thoughts, . 246
He asked, 'Is this the only dead man, or does the world contain like instances?' Replying thus he said, 'All, everywhere, the same; he who begins his life must end it likewise; . 247
'The strong and lusty and the middle-aged, having a body, cannot but decay (and die).' The prince now harassed and perplexed in mind; his body bent upon the chariot leaning-board, . 248
With bated breath and struggling accents, stammered thus, 'Oh worldly men! how fatally deluded! beholding everywhere the body brought to dust, yet everywhere the more carelessly living; . 249
'The heart is neither lifeless wood nor stone, and yet it thinks not "all is vanishing!"' Then turning, he directed his chariot to go back, and no longer waste his time in wandering. . 250
How could he, whilst in fear of instant death, go wandering here and there with lightened heart! The charioteer remembering the king's exhortation feared much nor dared go back; . 251
Straightforward then he pressed his panting steeds, passed onward to the gardens, (came to) the groves and babbling streams of crystal water, the pleasant trees, spread out with gaudy verdure, . 252
The noble living things and varied beasts so wonderful, the flying creatures and their notes melodious, all charming and delightful td the eye and ear, even as the heavenly Nandavana. . 253
VARGA 4. PUTTING AWAY DESIRE.
The prince on entering the garden, the women came around to pay him court; and to arouse in him thoughts frivolous; with ogling ways and deep design, . 254
Each one setting herself off to best advantage; or joining together in harmonious concert, clapping their hands, or moving their feet in unison, or joining close, body to body, limb to limb; . 255
Or indulging in smart repartees, and mutual smiles; or assuming a thoughtful saddened countenance, and so by sympathy to please the prince, and provoke in him a heart affected by love. . 256
But all the women beheld the prince, clouded in brow, and his godlike body not exhibiting its wonted signs of beauty; fair in bodily appearance, surpassingly lovely 1, . 251
All looked upwards as they gazed, as when we call upon the moon Deva to come 2; but all their subtle devices 3 were ineffectual to move Bodhisattva's heart. . 258
At last commingling together they join and look astonished and in fear, silent without a word. Then there was a Brahmaputra, whose name was called Udâyi 4 (Yau-to-i). . 259
(He) addressing the women, said, 'Now all of
p. 39
you, so graceful and fair, (see if you cannot) by your combined power hit on some device; for beauty's power is not for ever. . 260
'Still it holds the world in bondage, by secret ways and lustful arts; but no such loveliness in all the world (as yours), equal to that of heavenly nymphs 1; . 261
'The gods beholding it would leave their queens, spirits and Rishis would be misled by it; why not then the prince, the son of an earthly king 2? why should not his feelings be aroused? . 262
'This prince indeed, though he restrains his heart and holds it fixed 3, pure-minded, with virtue uncontaminated, not to be overcome by power of women; . 263
'(Yet) of old there was Sundarî (Su-to-li) able to destroy the great Rishi, and to lead him to indulge in love, and so degrade his boasted eminence 4; . 264
'Undergoing long penance, Gautama fell likewise (by the arts of) a heavenly queen; Shing-kü, a Rishi putra, practising lustful indulgences according to fancy 5, (was lost). . 265
'The Brahman Rishi Visvâmitra (Pi-she-po), living religiously 6 for ten thousand years, deeply
p. 40
ensnared by a heavenly queen, in one day was completely shipwreck’d in faith 1; . 266
'Thus those enticing women, by their power, overcame the Brahman ascetics how much more may ye, by your arts, overpower (the resolves) of the king's son; . 267
'Strive therefore after new devices 2, let not the king fail in a successor to the throne; women, altho’ naturally weak 3, are high and potent in the way of ruling men. . 268
'What may not their arts accomplish in promoting in men a lustful (impure) desire?' At this time all the attendant women, hearing throughout the words of Udâyi, . 269
Increasing their powers of pleasing, as the quiet horse when touched by the whip, went into the presence of the royal prince, and each one strove in the practice of every kind of art, . 270
(They) joined in music and in smiling conversation, raising their eyebrows, showing their white teeth, with ogling looks, glancing one at the other, their light drapery exhibiting their white bodies, . 271
Daintily moving with mincing gait, acting the part of a bride as if coming gradually nearer 4, desiring to promote in him a feeling of love, remembering the words of the great king 5, . 272
p. 41
'With dissolute form and slightly clad, forgetful of modesty and womanly reserve.' The prince with resolute heart was silent and still, with unmoved face (he sat); . 273
Even as the great elephant-dragon, whilst the entire herd moves round him 1; so nothing could disturb or move his heart, dwelling in their midst as in a confined room 2. . 274
Like the divine Sakra, around whom all the Devîs assemble, so was the prince as he dwelt in the gar-dens; (the maidens) encircling him thus; . 275
Some arranging their dress, others washing their hands or feet, others perfuming their bodies with scent, others twining flowers for decoration, . 276
Others making strings for jewelled necklets, others rubbing or striking their bodies, others resting, or lying, one beside the other, others, with head inclined, whispering secret words, . 277
Others engaged in common sports, others talking of amorous things, others assuming lustful attitudes, striving thus to move his heart; . 278
But Bodhisattva, peaceful and collected, firm as a rock, difficult to move, hearing all these women's talk, unaffected either to joy or sorrow, . 279
Was driven still more to serious thought, sighing to witness such strange conduct, and beginning to understand the women's design, by these means to disconcert his mind, . 280
'Not knowing that youthful beauty soon falls, destroyed by old age and death, fading and perishing! This is the great distress! What ignorance
p. 42
and delusion (he reflected) overshadow their minds, . 281
'Surely they ought to consider old age, disease, and death, and day and night stir themselves up to exertion, whilst this sharp double-edged sword hangs over the neck. What room for sport or laughter, . 282
'Beholding those (monsters) old age, disease, and death? A man who is unable to resort to this inward knowledge, what is he but a wooden or a plaster man, what heart-consideration in such a case! . 283
'Like the double tree that appears in the desert, with leaves and fruit all perfect and ripe, the first cut down and destroyed, the other unmoved by apprehension, . 284
'So it is in the case of the mass of men, they have no understanding either!' At this time Udâyi came to the place where the prince was, . 285
And observing his silent and thoughtful mien, unmoved by any desire for indulgence (the five desires), he forthwith addressed the prince, and said, 'The Mahâraga, by his former appointment 1, . 286
'Has selected me to act as friend to his son; may I therefore speak some friendly words? an enlightened friendship (or, friend) is of three sorts, that which removes things unprofitable, . 287
'Promotes that which is real gain, and stands by a friend in adversity. I claim the name of
p. 43
[paragraph continues] "enlightened friend," and would renounce all that is magisterial, . 288
'But yet not speak lightly or with indifference. What then are the three sources of advantage? listen, and I will now utter true words, and prove myself a true and sincere adviser. . 289
'When the years are fresh and ripening, beauty and pleasing qualities in bloom, not to give proper weight to woman's influence, this is a weak man's policy (body) 1. . 290
'It is right sometimes to be of a crafty mind, submitting to those little subterfuges, which find a place in the heart's undercurrents, and obeying what those thoughts suggest, . 291
'In way of pleasures to be got from dalliance, this is no wrong in woman's (eye)! even if now the heart has no desire, yet it is fair to follow such devices; . 292
'Agreement (acquiescence) is the joy of woman's heart, acquiescence is the substance (the full) of true adornment; but if a man reject these overtures, he's like a tree deprived of leaves and fruits; . 293
'Why then ought you to yield and acquiesce? that you may share in all these things. Because in taking, there's an end of trouble--no light and changeful thoughts then worry us--294
'For pleasure is the first and foremost thought of all, the gods themselves cannot dispense with it. Lord Sakra was drawn by it to love the wife of Gautama the Rishi; . 295
'So likewise the Rishi Agastya, through a long
p. 44
period of discipline 1, practising austerities, from hankering after a heavenly queen (Devî), lost all reward of his religious endeavours, 296°
'The Rishi Brihaspati, and Kandradeva putra; the Rishi Parâsara, and Kavañgara (Kia-pin-ke-lo) 2: . 297
'All these, out of many others, were overcome by woman's love. How much more then, in your case, should you partake in such pleasant joys; . 298
'Nor refuse, with wilful heart, to participate in the worldly delights, which your present station, possessed of such advantages, offers you, in the presence of these attendants.' . 299
At this time the royal prince, hearing the words of his friend Udâyi, so skilfully put, with such fine distinction, cleverly citing worldly instances, . 300
Answered thus to Udâyi: 'Thank you for having spoken sincerely to me, let me likewise answer you in the same way, and let your heart suspend its judgment whilst you listen; . 301
'It is not that I am careless about beauty, or am ignorant of (the power of) human joys, but only that I see on all the impress of change; therefore my heart is sad and heavy; . 302
'If these things were sure of lasting, without the ills of age, disease, and death, then would I too take my fill of love; and to the end find no disgust or sadness; . 303
'If you will undertake to cause these women's beauty not after-while to change or wither, then, though the joy of love may have its evil, still it might hold the mind in thraldom; . 304
('To know that other) men grow old, sicken, and
p. 45
die, would be enough to rob such joys of satisfaction; yet how much more in their own case (knowing this) would discontentment fill the mind; . 305
'(To know) such pleasures hasten to decay, and their bodies likewise; if, notwithstanding this, men yield to the power of love, their case indeed is like the very beasts. . 306
'And now you cite the names of many Rishis, who practised lustful ways in life; their cases likewise cause me sorrow, for in that they did these things, they perished. . 307
'Again, you cite the name of that illustrious king, who freely gratified his passions, but he, in like way, perished in the act; know, then, that he was not a conqueror (Gina); . 308
'With smooth words to conceal an intrigue, and to persuade one's neighbour to consent, and by consenting to defile his mind; how can this be called a just device? . 309
'It is but to seduce one with a hollow lie,--such ways are not for me to practise; or, for those who love the truth and honesty; for they are, forsooth, unrighteous ways, . 310
'And such a disposition is hard to reverence; shaping one's conduct after one's likings, liking this or that, and seeing no harm in it, what method of experience is this! . 311
'A hollow compliance, and a protesting heart, such method is not for me to follow; but this I know, old age, disease, and death, these are the great afflictions which accumulate, . 312
And overwhelm me with their presence; on these I find no friend to speak, alas! alas! Udâyi! these, after all, are the great concerns; . 313
p. 46
'The pain of birth, old age, disease, and death; this grief is that we have to fear; the eyes see all things falling to decay, and yet the heart finds joy in following them; . 314
'But I have little strength of purpose, or command; this heart of mine is feeble and distraught, reflecting thus on age, disease, and death. Distracted, as I never was before; . 315
'Sleepless by night and day, how can I then indulge in pleasure? Old age, disease, and death consuming me, their certainty beyond a doubt, . 316
'And still to have no heavy thoughts, in truth my heart would be a log or stone.' Thus the prince, for Uda's sake, used every kind of skilful argument, . 317
Describing all the pains of pleasure; and not perceiving that the day declined. And now the waiting women all, with music and their various attractions, . 318
Seeing that all were useless for the end, with shame began to flock back to the city; the prince beholding all the gardens, bereft of their gaudy ornaments, . 319
The women all returning home, the place becoming silent and deserted, felt with twofold strength the thought of impermanence. With saddened mien going back, he entered his palace; . 320
The king, his father, hearing of the prince, his heart estranged from thoughts of pleasure, was greatly overcome with sorrow, and like a sword it pierced his heart. . 321
Forthwith assembling all his council, he sought of them some means to gain his end; they all replied, 'These sources of desire are not enough to hold and captivate his heart.' . 322
VARGA 5. LEAVING THE CITY.
And so the king increased the means for gratifying the appetite for pleasure; both night and day the joys of music wore out the prince, opposed to pleasure; . 323
Disgusted with them, he desired their absence, his mind was weaned from all such thoughts, he only thought of age, disease, and death; as the lion wounded by an arrow. . 324
The king then sent his chief ministers, and the most distinguished of his family, young in years and eminent for beauty, as well as for wisdom and dignity of manners, . 325
To accompany, and rest with him, both night and day, in order to influence the prince's mind. And now within a little interval, the prince again requested the king that he might go abroad. . 326
Once more the chariot and the well-paced horses were prepared, adorned with precious substances and every gem; and then with all the nobles, his associates, surrounding him, he left the city gates: . 327
Just as the four kinds of flower 1, when the sun shines, open out their leaves, so was the prince in all his spiritual splendour; effulgent in the beauty of his youth time; . 328
As he proceeded to the gardens from the city, the road was well prepared, smooth, and wide, the trees were bright with flowers and fruit, his heart was joyous, and forgetful of its care. . 329
p. 48
Now by the roadside as he beheld the ploughmen, plodding along the furrows, and the writhing worms, his heart again was moved with piteous feeling, and anguish pierced his soul afresh; . 330
To see those labourers at their toil, struggling with painful work, their bodies bent, their hair dishevelled, the dripping sweat upon their faces, their persons fouled with mud and dust; . 331
The ploughing oxen, too, bent by the yokes, their lolling tongues and gaping mouths; the nature of the prince, loving, compassionate, his mind conceived most poignant sorrow, . 332
And nobly moved to sympathy, he groaned with pain; then stooping down he sat upon the ground, and watched this painful scene of suffering; reflecting on the ways of birth and death! . 333
'Alas! he cried, for all the world! how dark and ignorant, void of understanding!' And then to give his followers chance of rest, he bade them each repose where’er they list; . 334
Whilst he beneath the shadow of a Gambu tree, gracefully seated, gave himself to thought. He pondered on the fact of life and death, inconstancy, and endless progress to decay. . 335
His heart thus fixed without confusion, the five desires (senses) covered and clouded over, lost in possession of enlightenment and insight, he entered on the first pure state of ecstacy. . 336
All low desire removed, most perfect peace ensued; and fully now in Samâdhi (he saw) the misery and utter sorrow of the world; the ruin wrought by age; disease, and death; . 337
The great misery following on the body's death and yet men not awakened to the truth! oppressed
p. 49
with others' suffering (age, disease, and death), this load of sorrow weigh’d his mind; . 338
'I now will seek (he said) a noble law, unlike the worldly methods known to men, I will oppose disease and age and death, and strive against the mischief wrought by these on men.' . 339
Thus lost in tranquil contemplation, (he considered that) youth, vigour, and strength of life, constantly renewing themselves, without long stay, in the end fulfil the rule of ultimate destruction; . 340
(Thus he pondered) without excessive joy or grief, without hesitation or confusion of thought, without dreaminess or extreme longing, without aversion or discontent, . 341
But perfectly at peace, with no hindrance, radiant with the beams of increased illumination. At this time a Deva of the Pure abode, transforming himself into the shape of a Bhikshu, . 342
Came to the place where the prince was seated; the prince with due consideration rose to meet him, and asked him who he was. In reply he said, 'I am a Shâman, . 343
'Depressed and sad at thought of age, disease, and death, I have left my home to seek some way of rescue, but everywhere I find old age, disease, and death, all (things) hasten to decay and there is no permanency; . 344
'Therefore I search for the happiness of something that decays not, that never perishes, that never knows beginning, that looks with equal mind on enemy and friend, that heeds not wealth nor beauty, . 345
'The happiness of one who finds repose alone in
p. 50
solitude, in some unfrequented dell, free from molestation, all thoughts about the world destroyed, dwelling in some lonely hermitage, . 346
'Untouched by any worldly source of pollution, begging for food sufficient for the body.' And forthwith as he stood before the prince, gradually rising up he disappeared in space. . 347
The prince with joyful mind, considering, recollected former Buddhas, established thus in perfect dignity of manner; with noble mien and presence, as this visitor. . 348
Thus calling things to mind with perfect self-possession, he reached the thought of righteousness, and by what means it can be gained. Indulging thus for length of time in thoughts of religious solitude, . 349
He now suppressed his feelings and controlled his members, and rising turned again towards the city. His followers all flocked after him, calling him to stop and not go far from them, . 350
But in his mind these secret thoughts so held him, devising means by which to escape from the world, that tho’ his body moved along the road, his heart was far away among the mountains; . 351
Even as the bound and captive elephant, ever thinks about his desert wilds. The prince now entering the city, there met him men and women, earnest for their several ends; . 352
The old besought him for their children, the young sought something for the wife, others sought something for their brethren; all those allied by kinship or by family, . 353
Aimed to obtain their several suits, all of them joined in relationship dreading the pain (expectation)
p. 51
of separation. And now the prince's heart was filled with joy, as he suddenly heard those words 'separation and association.' . 354
'These are joyful sounds to me,' he said, 'they assure me that my vow shall be accomplished.' Then deeply pondering the joy of 'snapped relationship,' the idea of Nirvâna, deepened and widened in him 1, . 355
His body as a peak of the Golden Mount, his shoulder like the elephant's, his voice like the spring-thunder, his deep-blue eye like that of the king of oxen, . 356
His mind full of religious thoughts (aims), his face bright as the full moon, his step like that of the lion king, thus he entered his palace, . 357
Even as the son of Lord Sakra (or, Sakra-putra) his mind reverential, his person dignified, he went straight to his father's presence, and with head inclined, enquired, 'Is the king well?' . 358
Then he explained his dread of age, disease, and death, and sought respectfully permission to become a hermit. 'For all things in the world' (he said), 'though now united, tend to separation;' . 359
Therefore he prayed to leave the world; desiring to find 'true deliverance.' His royal father hearing the words 'leave the world,' was forthwith seized with great heart-trembling, . 360
Even as the strong wild elephant shakes with his weight the boughs of some young sapling; going forward, seizing the prince's hands, with falling tears, he spake as follows: . 361
p. 52
'Stop! nor speak such words, the time is not yet come for "a religious life," you are young and strong, your heart beats full, to lead a religious life frequently involves trouble, . 362
'It is rarely possible to hold the desires in check, the heart not yet estranged from their enjoyment; to leave your home and lead a painful ascetic life, your heart can hardly yet resolve on such a course; . 363
'To dwell amidst the desert wilds or lonely dells, this heart of yours would not be perfectly at rest, for though you love religious matters, you are not yet like me in years; . 364
'You should undertake the kingdom's government, and let me first adopt ascetic life; but to give up your father and your sacred duties, this is not to act religiously; . 365
'You should suppress this thought of "leaving home," and undertake your worldly duties, find your delight in getting an illustrious name, and after this give up your home and family.' . 366
The prince, with proper reverence and respectful feelings, again besought his royal father; but promised if he could be saved from four calamities, that he would give up the thought of 'leaving home;' . 367
If he would grant him life without end, no disease, nor undesirable old age, and no decay of earthly possessions; then he would obey and give up the thought of 'leaving home.' . 368
The royal father then addressed the prince, 'Speak not such words as these, for with respect to these four things, who is there able to prevent them, or say nay to their approach; . 369
p. 53
'Asking such things as these (four things), you would provoke men's laughter! But put away this thought of "leaving home," and once more take yourself to pleasure.' . 370
The prince again besought his father, 'If you may not grant me these four prayers, then let me go I pray, and leave my home. O! place no difficulties in my path; . 371
'Your son is dwelling in a burning house, would you indeed prevent his leaving it! To solve a doubt is only reasonable, who could forbid a man to seek its explanation? . 372
'Or if he were forbidden, then by self-destruction he might solve the difficulty, in an unrighteous way: and if he were to do so, who could restrain him after death?' . 373
The royal father, seeing his son's mind so firmly fixed that it could not be turned, and that it would be waste of strength to bandy further words or arguments, . 374
Forthwith commanded more attendant women, to provoke still more his mind to pleasure; day and night (he ordered them) to keep the roads and ways, to the end that he might not leave his palace; . 375
(He moreover ordered) all the ministers of the country to come to the place where dwelt the prince, to quote and illustrate the rules of filial piety, hoping to cause him to obey the wishes of the king. . 376
The prince, beholding his royal father bathed with tears and o’erwhelmed with grief, forthwith returned to his abode, and sat himself in silence to consider; . 377
p. 54
All the women of the palace, coming towards him, waited as they circled him, and gazed in silence on his beauteous form. They gazed upon him not with furtive glance, . 378
But like the deer in autumn brake looks wistfully at the hunter; around the prince's straight and handsome form, (bright) as the mountain of true gold (Sumeru), . 379
The dancing women gathered doubtingly, waiting to hear him bid them sound their music; repressing every feeling of the heart through fear, even as the deer within the brake; . 380
Now gradually the day began to wane, the prince still sitting in the evening light, his glory streaming forth in splendour, as the sun lights up Mount Sumeru; . 381
Thus seated on his jewelled couch, surrounded by the fumes of sandal-wood, the dancing women took their places round; then sounded forth their heavenly (Gandharva) music, . 382
Even as Vaisaman (Vaisravana) produces every kind of rare and heavenly sounds. The thoughts which dwelt within the prince's mind entirely drove from him desire for music, . 383
And tho’ the sounds filled all the place, they fell upon his ear unnoticed. At this time the Deva of the Pure abode, knowing the prince's time was come, . 384
The destined time for quitting home, suddenly assumed a form and came to earth, to make the shapes of all the women unattractive, so that they might create disgust, . 385
And no desire arise from thought of beauty. Their half-clad forms bent in ungainly attitudes,
p. 55
forgetful in their sleep, their bodies crooked or supine, the instruments of music lying scattered in disorder; . 386
Leaning and facing one another, or with back to back, or like those beings thrown into the abyss, their jewelled necklets bound about like chains, their clothes and undergarments swathed around their persons; . 387
Grasping their instruments, stretched along the earth, even as those undergoing punishment at the hands of keepers (eunuchs), their garments in confusion, or like the broken kani flower (poppy?); . 388
Or some with bodies leaning in sleep against the wall, in fashion like a hanging bow or horn, or with their hands holding to the window-frames, and looking like an outstretched corpse; . 389
Their mouths half opened or else gaping wide, the loathsome dribble trickling forth, their heads uncovered and in wild disorder, like some unreasoning madman's; . 390
The flower wreaths torn and hanging across their face, or slipping off the face upon the ground; others with body raised as if in fearful dread, just like the lonely desert(?) bird; . 391
Or others pillowed on their neighbour's lap, their hands and feet entwined together, whilst others smiled or knit their brows in turn, some with eyes closed and open mouth, . 392
Their bodies lying in wild disorder, stretched here and there, like corpses thrown together. And now the prince seated, in his beauty, looked with thought on all the waiting women; . 393
Before, they had appeared exceeding lovely, their laughing words, their hearts so light and gay, their
p. 56
forms so plump and young, their looks so bright; but now, how changed! so uninviting and repulsive. . 394
And such is woman's disposition! how can they, then, be ever dear, or closely trusted; such false appearances! and unreal pretences; they only madden and delude the minds of men. . 395
And now (he said), 'I have awakened to the truth! Resolved am I to leave such false society.' At this time the Deva of the Pure abode descended and approached, unfastening the doors. . 396
The prince, too, at this time rose and walked along, amid the prostrate forms of all the women; with difficulty reaching to the inner hall, he called to Kandaka, in these words, . 397
'My mind is now athirst and longing for the draught of the fountain of sweet dew, saddle then my horse, and quickly bring it here. I wish to reach the deathless city; . 398
'My heart is fixed beyond all change, resolved I am and bound by sacred oath; these women, once so charming and enticing, now behold I altogether loathsome; . 399
'The gates, which were before fast-barred and locked, now stand free and open! these evidences of something supernatural, point to a climax of my life.' . 400
Then Kandaka stood reflecting inwardly, whether to obey or not the prince's order, without informing his royal father of it, and so incur the heaviest punishment. . 401
The Devas then gave spiritual strength; and unperceived the horse equipped came round, with even pace; a gallant steed, with all his jewelled trappings for a rider; . 402
p. 57
High-maned, with flowing tail, broad-backed, short-haired and ear’d, with belly like the deer's, head like the king of parrots, wide forehead, round and claw-shaped nostrils, . 403
Breath like the dragon's, with breast and shoulders square, true and sufficient marks of his high breed. The royal prince, stroking the horse's neck, and rubbing down his body, said, . 404
'My royal father ever rode on thee, and found thee brave in fight slid fearless of the foe; now I desire to rely on thee alike! to carry me far off to the stream (ford) of endless life, . 405
'To fight against and overcome the opposing force of men, the men who associate in search of pleasure, the men who engage in the search after wealth, the crowds who follow and flatter such persons; . 406
'In opposing sorrow, friendly help is difficult (to find), in seeking religious truth there must be rare enlightenment, let us then be knit together thus as friends; then, at last, there will be rest from sorrow. . 407
'But now I wish to go abroad, to give deliverance from pain; now then, for your own sake it is, and for the sake of all your kind, . 408
'That you should exert your strength, with noble pace, without lagging or weariness.' Having thus exhorted him, he bestrode his horse, and grasping the reins, proceeded forth; . 409
The man like the sun shining forth from his tabernacle (sun-palace streams), the horse like the white floating cloud (the white cloud-pile), exerting himself but without exciting haste, his breath concealed and without snorting; . 410
Four spirits (Devas) accompanying him, held up
p. 58
his feet, heedfully concealing (his advance), silently and without noise; the heavy gates fastened and barred (locked), the heavenly spirits of themselves caused to open; . 411
Reverencing deeply the virtuous (sinless) father, loving deeply the unequalled son, equally affected with love towards all the members of his family (these. Devas took their place). . 412
Suppressing his feelings, but not extinguishing his memory, lightly he advanced and proceeded beyond the city, pure and spotless as the lily flowers which spring from the mud; . 413
Looking up with earnestness at his father's palace, he announced his purpose--unwitnessed and unwritten--'If I escape not birth, old age, and death, for evermore I pass not thus along;' . 414
All the concourse of Devas, the space-filling Nâgas and spirits followed joyfully and exclaimed Well! well! (sâdhu), in confirmation of the true words (he spoke); . 415
The Nâgas and the company of Devas acquired a condition of heart difficult to obtain, and each with his own inherent light led on the way shedding forth their brightness. . 416
Thus man and horse both strong of heart went onwards, lost to sight, like streaming stars, but ere the eastern quarter flashed with light, they had advanced three yoganas. . 417
Footnotes
1:1 The Ikshvâku (sugar-cane) family of Potala. Suddhodana was the father of the Bodhisattva.
1:2 Wou-shing; this is the equivalent for the Agitavatî (river). But it here refers to the Sâkyas, as a race of Kakravartin monarchs.
1:3 Or, like Sakra, king of Devas, the husband of Sakî.
2:1 Here there seems to be a play on the word wan
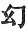
, which is the equivalent for Mâyâ or illusion. The Sanskrit text reads Mâyâpagatâ-iva Mâyâ, i.e. Mâyâ without deceit.
2:2 Or, (the season for) religiously observing the rules of abstinence.
2:3 Aurva.
2:4 Prithu, born from the arm of Vena.
2:5 Mândhâtri.
3:1 Kakshîvat. These names are supplied from the Sanskrit text.
3:2 This may also be translated 'as one who falls from space,' i.e. miraculously born from space.
3:3 He passed from the womb to be born. The idea seems to be that though conceived in the womb, he was born supernaturally from the side.
3:4 Kwan-tsai, weighed and considered.
3:5 These seven steps are frequently figured by seven lotus-marks. I-tsing refers to such marks at Nâlanda, where Buddha walked seven steps, forward and backward; they are also figured on the p. 4 cloth held by the attendants at the birth of Bodhisattva. See Tree and Serpent Worship, plate lxv, figure 2, middle scene.
4:1 This birth is a Buddha-birth.
4:2 He was thus consecrated to be a king; see Childers, Pâli Dict., sub Abhisiñkati; also Eitel, Handbook, sub Mûrddhâbhishikta.
4:3 Inviting him to perfect the way of Buddha.
4:4 That is, 'to advance the cause of true religion.'
5:1 The Suddha-vâsas, 'beings dressed in pure garments.' A class of heavenly beings, supposed to take peculiar interest in the religious welfare of men.
5:2 'Creation,' in the sense of 'all that lives.'
5:3 Sumeru, written also Sumě and Meru. The primeval mountain; the Alborz, Atlas, or Olympus of other tribes. It is explained as 'the high, or resplendent, mountain.' On it was the heaven of the gods (the thirty-three gods).
5:4 It would seem from this that the original idea of Sumeru was 'the mountain of Heaven;' the visible heaven, or firmament, which 'firmly holds the earth.'
6:1 Mâra, the king of the world of desire. According to the Buddhist theogony he is the god of sensual love. He holds the p. 7 world in sin. He was the enemy of Buddha, and endeavoured in every way to defeat him. He is also described as the king of death.
7:1 Beholding his 'born son,' or 'begotten son.'
7:2 K’i-teh, truly unique (Williams' Diet.) Mi tsang yau, unseen before, miraculous.
7:3 The text seems to point to alternately recurring hope and grief.
7:4 The text here is difficult. I take Khang-suh to be equal to Khang-yê, which is a frequent expression to denote the 'long night' of transmigration or ignorance. If this be not so, then Khang-suh may be simply 'aged.'
7:5 Khi Siang, a discerner of signs or portents.
7:6 That is, either the signs on the child's body, or the occurrences attending his birth.
8:1 Or, a most victorious son; or, a son most renowned.
8:2 K’i-teh, truly unique; strange or wonderful; (p. 7, n. 2.)
8:3 Increasing or advancing prosperity.
8:4 Must assuredly save the world.
8:5 A body, such a masterpiece.
8:6 Khing-hsio, perfect illumination, Samyak-Sambuddha; or, as in the text.
8:7 A wheel-turning monarch. A monarch like the sun 'that flies as he goes;' the old conceit of a king of the age of gold a; the expectation of peace and prosperity resulting from the universal authority of such a righteous king, is an old, perhaps a primitive, one. The Kakravartin is the eastern form of the myth.
8:a That is, probably, 'a golden (wheel) king.'
9:1 The four empires, that is, the four continents or quarters of the world.
9:2 Deliverance, that is, from sin; or sorrow the result of sin (moksha).
9:3 Shine universally; as the light of the sun.
9:4 The ocean is always in Buddhist works, as in Homer, associated with 'flowings.' The expression in the Chinese, liu-hai, corresponds exactly with Ὠκεανοῖο ῥέεθρα.
9:5 The most worshipful.
9:6 Widening more and more.
9:7 Of a deep purple or violet colour,
10:1 That is, the Brahman wearing the twice-born thread.
10:2 Or, whatever is born according to the nature of things.
10:3 I restore these names according to the Sanskrit text, supplied by Professor Max Miller.
10:4 That is, belonging to the Rishi tribe; in other words, 'these two Rishis.'
10:5 Or, it may, perhaps more correctly, be rendered 'separated by a long period from Sutras or Shâstras,' or, when these works had long been lost.
10:6 Is this Parâsara, the reputed father of Vyâsa? (see Max Müller's Ancient Sanskrit Literature, p. 479.)
10:7 Illustrious Sûtras (Ming King) may possibly refer to the Vedas, but the five vidyâs are also called by this name (Jul. II, 73).
11:1 That is, the first of the Ikshvâku monarchs who reigned at Potala (Tatta) at the mouth of the Indus.
11:2 Or, were born by their own power.
11:3 Or, the former were better, the later inferior; the former inferior, the later better.
12:1 Or, extended his religious offerings.
12:2 Leaving my home will practise a pure (Brahman) life.
12:3 Practising austerities.
12:4 That is, 'purity' and 'penance.'
13:1 The Chinese symbol 'teh' properly means 'virtue,' as in the title of Laou Tseu's work, Tau-teh-king. But in Buddhist books it generally corresponds with the Sanskrit guna, in the sense of a 'quality' or 'characteristic.'
13:2 The expression suh khih points to conduct in former conditions of existence. It properly means 'a night's rest' or 'a lodging one night' (Williams), but in Buddhist books it commonly refers to abodes or conditions of life, occupied during the night (long night) of transmigration.
13:3 Following the way of the sun.
13:4 Complete the way of true wisdom (Sambodhi or Sambuddha).
13:5 Such miraculous portents going before. It would seem from Asita's description that he came from the East following the sun, and as he came he saw before him miraculous portents.
14:1 Or, his fingers and his toes.
14:2 That is, the ûrnâ. This white wool-like mark seems to have been derived in the first instance from the circle of hair on the forehead of the bull. Moschus describes the bull that carried off Europa as having this 'silver white circle' on his forehead.
15:1 The 'eternal draught' or 'sweet dew' of Ambrosia. This expression is constantly used in Buddhist writings. It corresponds with the Pâli amatam, which Childers explains as the 'drink of the gods.'
15:2 Or, if I have.
15:3 This sloka may be translated otherwise thus: 'A man among all his kindred loves deeply a spotless a son; at this time, in recollection thereof, speaking, cause me to revive;' or the latter lines may still be rendered, 'in memory of what you said before, cause me now, by speaking as before, to revive.'
15:a Wou-kwo-tseu; either 'a faultless son' or 'nothing beyond his son.'
16:1 This line may be also rendered 'because he has done with birth, therefore he is born.' The text is full of such double-meanings.
16:2 The five desires, or five appetites of sight, smell, taste, hearing, and touch.
17:1 The word 'salvation' corresponds to the Sanskrit moksha, deliverance or escape. The garden of Lumbinî is sometimes called the 'garden of deliverance,' because Maya was there delivered of her child.
17:2 Or, removed from an opportunity of reaping merit by the teaching of the holy one.
18:1 The condition of the highest Deva, according to Buddhism, does not exempt him from re-birth; subject to the calamities incident on such a renewal of life.
19:1 'Shing-tseu,' the born or begotten child.
19:2 I am unable to translate this line except literally,' two-feeding white pure ivory (or, tooth),' ’rh fan pih tsing ’nga. [I am informed, however, by Professor Max Müller that it refers to the 'elephant' The elephant is called dvipa, the twice-drinker, corresponding to ’rh fan (for ’rh yin), the double-feeder (drinker), in the Chinese.]
20:1 Na-lo-kiu-po. Nalakûvara was the son of Vaisravana.
20:2 Vessels of the seven precious (substances).
20:3 According to occasion in abundance produced. The expression 'tsah' may either refer to variety or number. Thus the p. 21 convocation of the Arhats at Vaisâlî is called 'tsah;' a miscellaneous collection of anecdotes or tales is called by the same name.
21:1 Or, every kind of party-colour’d horse.
21:2 Like the clouds.
22:1 This seems to mean that those who had not received benefit from the teaching of the four previous Buddhas, that even these were placable and well-disposed.
22:2 This is a difficult verse, it may be translated literally thus, 'All learned women (or, all the wives of sages) were profoundly grave as the fist man of the kalpa.' Whether it refers to the docility of the otherwise quarrelsome women, or to their gravity and learning, it is not easy to say.
23:1 The description here given of the peace and content prevailing in the world on the birth of Bodhisattva (and his name given to him in consequence) resembles the account of the golden age in classic authors.
23:2 Mâyâ is generally stated to have died after seven days from the birth of her child. But here the context seems to require a longer interval, as he was ten days old when taken to the temple. Mâyâ was born in the Trayastrimsas Heaven, or the Heaven of the Thirty-three Gods. The legend states that Buddha after his enlightenment proceeded there to convert her.
24:1 His mind resting on its high and excellent purpose; so at least the expression K’ai, domain or precinct, may sometimes be rendered. It means, 'within the limits of its own high excellent (purpose).'
25:1 That is, rising from the earth above other hills.
25:2 Gandharvas, heavenly musicians; muses.
25:3 With nobleness of purpose (gin) loving the transforming power of the true law. That is, leading a religious life.
25:4 That is, as I understand it, the king himself, for his son's sake, devoted himself to piety.
25:5 Or, by means of loving instruction subduing men's hearts; or, by love, teaching to subdue men's hearts.
26:1 Or, every kind of doctrine (magical art) that opposed religion.
26:2 Or, (he said) like as I desire rest for my child, so &c.
26:3 This and the whole of the context is obscure; the account evidently refers to Suddhodana; the line which I have translated 'loving righteous conversation' may be rendered 'loving conversation (or, converse), opposing a want of truth or righteousness (i),' or, 'loving an absence of all unrighteousness in conversation.' The next line, which is evidently in contrast with the previous one, may be translated, 'Righteous words, opposed to an absence of love.' The next line is, 'Loving words, opposed to that which is not true.' And then follows, 'Truthful words, opposed to that which is not love.'
27:1 I would rather translate these two lines thus, 'Not regarding so much the assemblies convoked for sacrificing to the gods, as excelling in the merit (happiness) of separation from worldly things;' or the word 'sse' may mean 'sacrifice' itself (as ποιέω in Greek), and then it would be 'excelling in merit without sacrifice.'
27:2 These four lines are enigmatical. They perhaps have some reference to the teaching of the seven Rishis, or the number seven may refer to the 'seven passions.'
28:1 Or, loving his son, and loving me also.
28:2 We have here a succession of lines in which there is a play on the word 'excellency' (shing), or 'victorious' (gina).
29:1 These verses are very obscure, and can only be understood by comparison with the Sanskrit.
29:2 In this section we have an account of the excursion of the royal prince without the precincts of the palace, and the sights which affected his mind with a desire to leave the world.
30:1 Otherwise, singing-women.
30:2 Or, thoughts of happiness.
31:1 As stars following the constellation-king.
34:1 How can a man. not (desire) to remove it (i.e. old age) as a hateful thing?
38:1 Surpassingly adorned or magnificent.
38:2 Or, as when the moon Deva (first) comes.
38:3 In every way practising subtle devices (upâya).
38:4 There is mention of Udâyi in the Fo-pen-hing-tsah-king, chap. W. See also note 1, p. 124, Romantic History of Buddha.
39:1 In appearance equal to Devîs.
39:2 Or, what then is man (to do), though son of a king, that his feelings should not be aroused?
39:3 Holding his will, though firmly fixed.
39:4 And bend his head beneath her feet.
39:5 The phrase which ends this line is obscure. It may be rendered thus, Shing-kü, the Rishi putra, practised lustful ways, beside the flowings of the fountain.' [See a similar case, Catena of Buddhist Scriptures, p. 259.] The Sanskrit text is as follows: 'Rishyasriṅga, the son of a Muni, unlearned with women.'
39:6 Practising religious rules, or, preparing a religious life.
40:1 Completely ruined. The name of the queen was Ghritâkî.
40:2 The Chinese 'fong pien' denotes the use of 'means to an end;' generally it can be rendered 'expedients.'
40:3 Or, the nature of women although weak.
40:4 So I understand the passage, as if a coy wife gradually approached -:'her husband.
40:5 Who the great king is I do not find, but I take the two lines following to be a quotation. [The great king was probably the father of Buddha.]
41:1 Or, surrounded by the entire herd.
41:2 That is, cramped in the midst of the encircling crowd of girls.
42:1 This passage is obscure; literally it is 'former--seeing--command.'
43:1 'This is the character of non-victorious men,' Again there is a play on the word 'Shing' a Gina. The Sanskrit renders it 'rudeness.' The Chinese fi-shing-gin may also mean coarse or unpolished.
44:1 'Kang-yê,' the long night.
44:2 The Sanskrit text has, 'Vasishtha begat Kapiñgalâda.'
47:1 It may be a description of some particular flower, 'four-seed (kind)-flower.'
51:1 Literally, 'deeply widened the mind of Nirvâna (Nî-pan).'
Giặc phiền não thường luôn rình rập giết hại người, độc hại hơn kẻ oán thù. Sao còn ham ngủ mà chẳng chịu tỉnh thức?Kinh Lời dạy cuối cùng
 » Tải tất cả bản dịch (file RTF)
» Hán văn » Phiên âm Hán Việt
» Càn Long (PDF, 0.7 MB) » Vĩnh Lạc (PDF, 0.77 MB)
» Tải tất cả bản dịch (file RTF)
» Hán văn » Phiên âm Hán Việt
» Càn Long (PDF, 0.7 MB) » Vĩnh Lạc (PDF, 0.77 MB)  » CBETA PDF (PDF, 0.77 MB)
» CBETA PDF (PDF, 0.77 MB) 
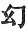 , which is the equivalent for Mâyâ or illusion. The Sanskrit text reads Mâyâpagatâ-iva Mâyâ, i.e. Mâyâ without deceit.
, which is the equivalent for Mâyâ or illusion. The Sanskrit text reads Mâyâpagatâ-iva Mâyâ, i.e. Mâyâ without deceit.